Voltmeter Symbol: Understanding its Importance and Applications
TheToolGeeks.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program and other affiliate advertising programs. We may earn from qualifying purchases. (Learn More).
At The Tool Geeks, where we’re dedicated to assisting you with DIY projects and providing recommendations for various power tools, we understand the importance of decoding symbols in the world of electrical instruments. Today, we shed light on the voltmeter symbol, an essential icon in the realm of electrical measurements.
So, grab your tool belt and let’s explore the world of voltmeters.
Jump To Page Contents:
Voltmeter Symbol: Understanding the Basics
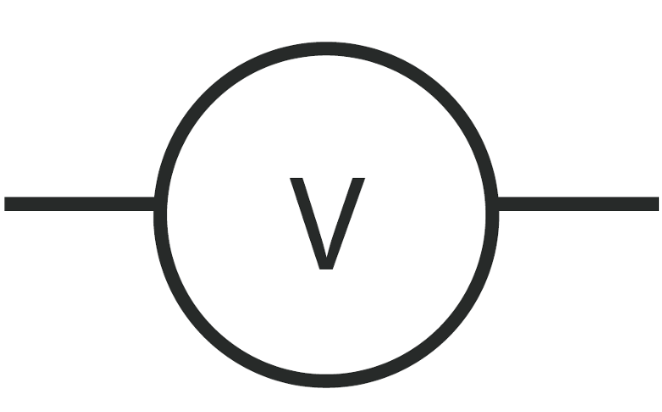
The voltmeter symbol is a visual representation that embodies the nature and purpose of this crucial device. Comprising a circle with a horizontal line inside and two diagonal lines extending from the circle’s top, the symbol holds a wealth of meaning.
The circle, often referred to as the ‘head,’ signifies the voltmeter itself – the instrument designed to measure the voltage between two points in an electric circuit. The horizontal line within the circle represents the needle or digital display responsible for indicating the voltage value.
Applications of Voltmeter Symbol
The voltmeter symbol finds extensive applications in various fields, such as:
- Electronics and Circuit Design
In electronics and circuit design, the voltmeter symbol is frequently employed in schematics to illustrate voltage measurements across different components. By understanding the voltage drops and potentials, engineers can optimize circuit performance and ensure safety.
- Electrical Testing and Troubleshooting
Electricians and technicians use voltmeters to diagnose and troubleshoot electrical issues. The voltmeter symbol serves as a visual representation of where the voltmeter should be connected to take accurate readings.
- Educational Purposes
In educational settings, the voltmeter symbol plays a crucial role in teaching students about electrical circuits and measurements. It simplifies complex concepts and aids in grasping the fundamentals of voltage and current.
The Role of the Voltmeter in Measuring Voltage
When integrated into an electrical circuit, the voltmeter gauges the disparity in voltage between two designated locations. It operates on the principle of a galvanometer, which uses the deflection of a pointer or needle to indicate voltage. By measuring voltage, engineers can analyze circuit performance, identify irregularities, and ensure the system operates within safe parameters.
Voltmeter vs. Multimeter
A voltmeter is an electrical measuring instrument that can measure voltage. A multimeter is a multi-function device that can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between voltmeters and multimeters:
| Feature | Voltmeter | Multimeter |
| Purpose | To measure voltage | To measure voltage, current, and resistance |
| Range | Typically measures voltage in the range of millivolts to kilovolts | Can measure voltage, current, and resistance in a wider range of values |
| Accuracy | Typically less accurate than multimeters | More accurate than voltmeters |
| Cost | Less expensive than multimeters | More expensive than voltmeters |
In general, a voltmeter is a good choice if you only need to measure voltage. A multimeter is a better choice if you need to measure voltage. current. and resistance.
Many voltmeters are now incorporated into multimeters due to the lower cost of and multifunctionality provided by multimeters.
Here are some additional things to consider when choosing between a voltmeter and a multimeter:
- Accuracy: If you need to measure voltage with a high degree of accuracy, then you should use a multimeter. Voltmeters are typically less accurate than multimeters.
- Cost: Voltmeters are less expensive than multimeters. If you only need to measure voltage occasionally, then a voltmeter may be a good option for you.
- Features: Multimeters have more features than voltmeters. If you need to measure current or resistance, then you will need a multimeter.
Applications of the Voltmeter Symbol in Different Fields
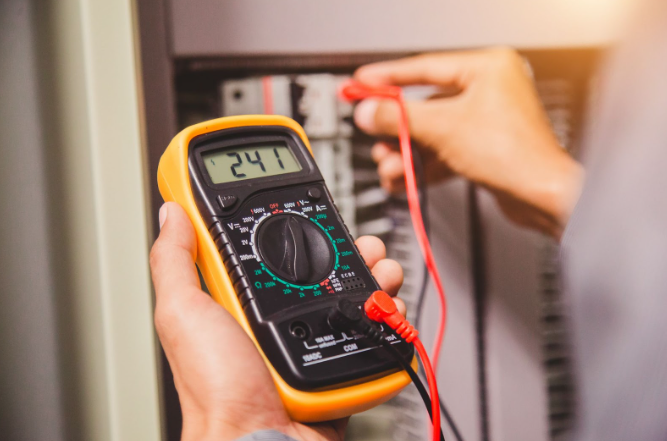

- Renewable Energy Systems
Within the realm of renewable energy systems like solar panels and wind turbines, the emblem of a voltmeter serves as a compass for technicians, steering them towards the realm of vigilant voltage oversight and adeptly enhancing the yield of power, thus fostering a realm of energy production marked by prowess and efficiency.
- Automotive Industry
In the automotive realm, the voltmeter symbol aids in diagnosing battery health and electrical system performance. Technicians rely on the symbol to ensure reliable vehicle operation.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure
Voltmeter symbols play a pivotal role in the maintenance of telecommunications infrastructure. Engineers use them to monitor voltage levels and ensure seamless communication networks.
How Does the Voltmeter Symbol Fit in with Power Tools?
The voltmeter symbol is used in power tools to indicate the voltage of the tool’s power source. This is important information for users to know, as it can help them to avoid using the tool with a voltage that is too high or too low for its intended use. For example, a power tool that is designed to operate at 12 volts should not be used with a power source that provides 24 volts, as this could damage the tool.
The voltmeter symbol is typically located on the power tool’s label or near the power switch. It is usually a capital “V” with a wavy line above it, which indicates that it is measuring alternating current (AC) voltage. Some power tools may also have a voltmeter symbol with three hyphens above it, which indicates that it is measuring direct current (DC) voltage.
If you are unsure of the voltage of a power tool, it is always best to consult the owner’s manual or contact the manufacturer. Using a power tool with the wrong voltage can be dangerous and can damage the tool.
Here are some examples of how the voltmeter symbol is used in power tools:
- A cordless drill may have a voltmeter symbol on its label to indicate the voltage of its battery.
- A circular saw may have a voltmeter symbol near the power switch to indicate the voltage of its power cord.
- A power inverter may have a voltmeter symbol on its front panel to indicate the output voltage of the inverter.
By understanding the voltmeter symbol, you can use power tools safely and avoid damaging them.
Types of Voltmeters
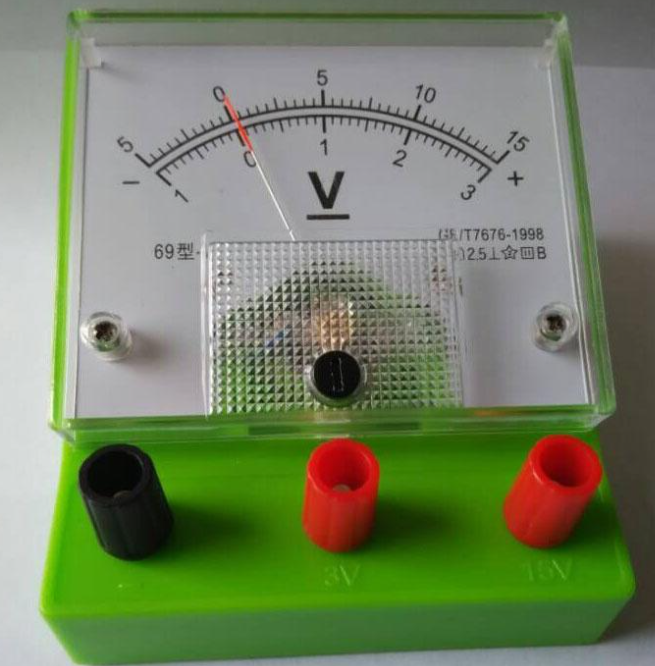

- Analog Voltmeters: The Classic Choice
Moving Coil Voltmeters (MCVs)
The Moving Coil Voltmeter, a fundamental type of analog voltmeter, relies on a suspended coil and a magnet to indicate voltage. It furnishes precise measurements of voltage, whether presented as direct current (DC) or as alternating current (AC).
Electrostatic Voltmeters
Electrostatic voltmeters utilize the principles of electrostatic attraction and repulsion to measure voltage. They offer excellent accuracy for low-voltage measurements and find applications in scientific research and precision testing.
- Digital Voltmeters (DVMs): Embracing the Digital Era
Ramp-Type DVMs
Ramp-type digital voltmeters determine the unknown voltage by measuring the time it takes for a linear voltage ramp to reach the same value. They provide fast measurements and are suitable for a wide range of voltage levels.
Integrating-Type DVMs
Integrating-type digital voltmeters integrate the input voltage over time to determine its magnitude. They are highly accurate for stable and slowly changing input voltages, making them suitable for precision applications.
- Autoranging Voltmeters: Adapting to Varied Magnitudes
Autoranging voltmeters automatically select the appropriate voltage range for the measured signal. By obviating the requirement for manual range calibration, these innovations enhance measurement efficiency while mitigating the chances of erroneously selecting an inappropriate range.
- True RMS Voltmeters: Precision in AC Measurements
True RMS voltmeters accurately measure the root mean square (RMS) value of an AC voltage waveform, regardless of its shape. They are essential for precise AC voltage measurements, especially in complex waveforms.
- High-Impedance Voltmeters: Minimizing Circuit Loading
High-impedance voltmeters have input resistance that is significantly higher than that of standard voltmeters. This minimizes the loading effect on the circuit being measured, ensuring accurate readings without disturbing the circuit’s behavior.
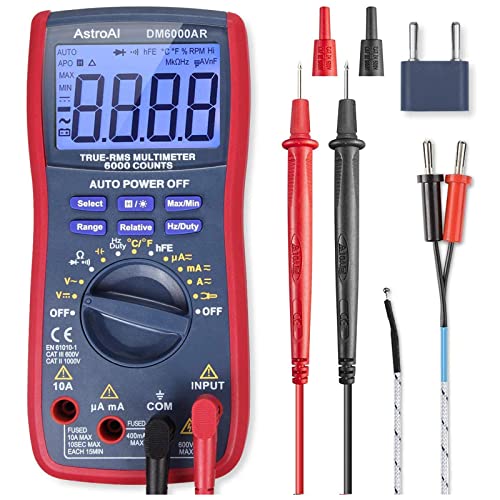
Recommended Voltmeters and Multimeters
- Multimeter measures up to 600V AC/DC voltage, 10A AC/DC current and 40 MOhms resistance
- Electrical tester measures temperature, capacitance, frequency, duty-cycle, and test diodes and continuity
- CAT III 600V safety rating
- Built to withstand a 3.3-foot (1 m) drop and withstand daily wear and tear on the job site
- Low battery indicator and easily accessible battery compartment
- For use in basic and controlled electromagnetic environments such as residential, business and light-industrial locations
- Includes test leads, thermocouple with adapter, batteries and user manual
- Accurately measures AC/DC Current, AC/DC Voltage, Capacitance, Frequency, Duty Cycle, Resistance, Diode, Continuity and Temperature
- Support Data Hold, Large LCD Backlit Screen, Auto Shut-off and Hanging Magnet, and Kickstand make the process of measurements easier.
- Professional level is reflected in some features include Auto-Ranging capability, and True RMS for measuring both AC Current and Voltage
- Troubleshoot a variety of automotive and household electrical problems safely and accurately.
- Double ceramic fuse is anti-burn and protects from overloading
- F400mA/600V and F10A/600V explosion-proof ceramic fuse tubes protect the multimeter effectively
CRAFTSMAN 3482141 8 Function Digital Multimeter
- Measures up to 600 volts alternating current and 10A alternating current for electrical installation home appliance repairs
- Measures up to 600 volts direct current and 10A direct current for auto marine and electronic installations or repairs
- Audible tone sounds below 30 ohms to check proper wiring and shorts
- Resistance is up to 2 megaohm for household and auto electrical wiring testing and repair
- Diode test for electronic and electrical testing
- VoltAlert technology for non-contact voltage detection
- AutoVolt automatic AC/DC voltage selection. DC millivolts - Range : 600.0 mV, Resolution : 0.1 mV
- Low input impedance: helps prevent false readings due to ghost voltage
- Large white LED backlight to work in poorly lit areas
- True RMS for accurate measurements on non-linear loads.Operating temperature:-10°C to +50°C.Battery life:400 hours typical, without backlight
- 3 1/2 digits, 7segment, 0.5"high LCD Display
- Max display: 1999, Auto polarity display
- Small and compact design
- Overload protection on all ranges
- Sampling 2~3 times readings per second
Gardner Bender GMT-318 Analog Multimeter, 6 Function, 14 Range, AC / DC Volt, 500V
- Manual range selection
- Easy to read, color-coded analog displays
- Includes replaceable test leads and operating instructions
- Agency approved with fuse overload protection circuitry incorporated
- 15 position rotary dial
Milwaukee 2213-20 Auto Voltage/Continuity Tester with Resistance
- Auto Voltage/Continuity Tester W/ Resistance
- The product is easy to use and easy to handle
- The product is highly durable
- Voltage tester automatically selects voltage or continuity; automatically powers on when any measurement is attempted
- Backlit LCD display
- CAT IV 600V modern solid-state design for safety
- Tests GFCI protected circuits
- Uses standard replaceable multimeter test leads
- Features built-in test lead holders on back of meter
- Integrated flashlight
Conclusion
The voltmeter symbol plays a pivotal role in the world of electrical engineering. It represents the voltmeter, an essential measuring instrument that helps engineers and technicians understand electrical potentials in circuits. By interpreting the symbol correctly and utilizing the voltmeter accurately, professionals can make informed decisions, troubleshoot issues, and ensure the efficient operation of electrical systems. Understanding the significance of the voltmeter symbol empowers individuals in the field of electrical engineering, enabling them to navigate complex circuits and contribute to advancements in technology.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.